Android Studio is the official Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for Android app development, based on IntelliJ IDEA. On top of IntelliJ’s powerful code editor and developer tools.
- A flexible Gradle-based build system
- A fast and feature-rich emulator
- A unified environment where you can develop for all Android devices
- Apply Changes to push code and resource changes to your running app without restarting your app
- Code templates and GitHub integration to help you build common app features and import sample code
- Extensive testing tools and frameworks
- Lint tools to catch performance, usability, version compatibility, and other problems
- C++ and NDK support
- Built-in support for Google Cloud Platform, making it easy to integrate Google Cloud Messaging and App Engine
Project structure
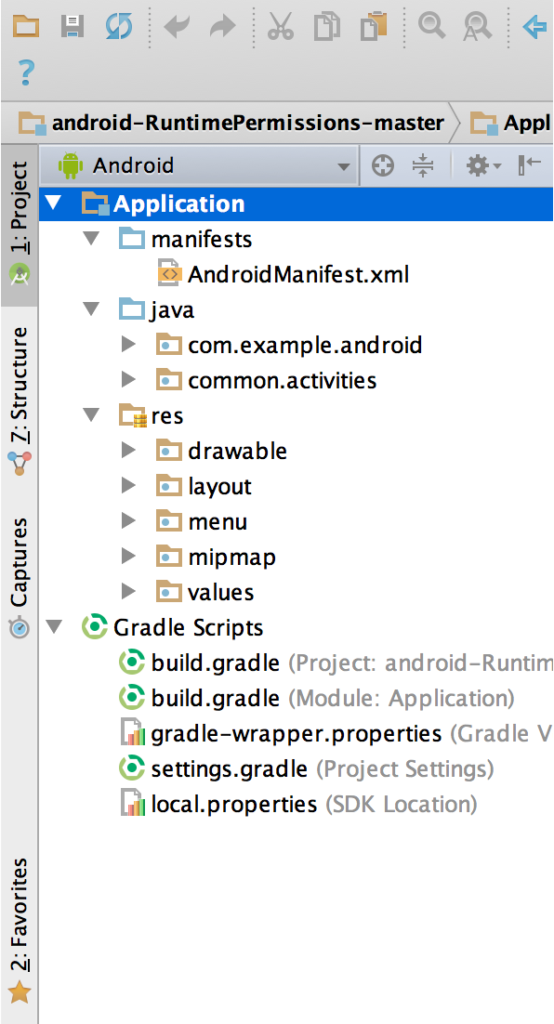
Each project in Android Studio contains one or more modules with source code files and resource files.
- Android app modules
- Library modules
- Google App Engine modules
All the build files are visible at the top level under Gradle Scripts and each app module contains the following folders:
- manifests: Contains the AndroidManifest.xml file.
- java: Contains the Java source code files, including JUnit test code.
- res: Contains all non-code resources, such as XML layouts, UI strings, and bitmap images.
The user interface
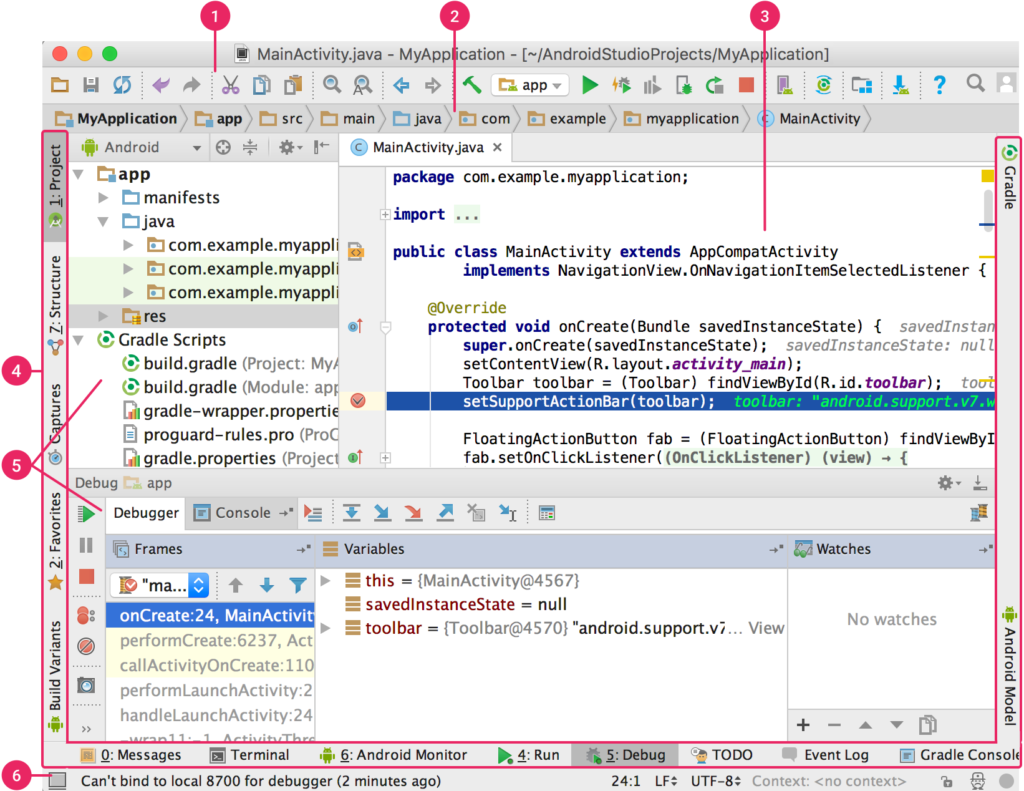
The Android Studio main window is made up of several logical areas
- The toolbar lets you carry out a wide range of actions, including running your app and launching Android tools.
- The navigation bar helps you navigate through your project and open files for editing. It provides a more compact view of the structure visible in the Project window.
- The editor window is where you create and modify code. Depending on the current file type, the editor can change. For example, when viewing a layout file, the editor displays the Layout Editor.
- The tool window bar runs around the outside of the IDE window and contains the buttons that allow you to expand or collapse individual tool windows.
- The tool windows give you access to specific tasks like project management, search, version control, and more. You can expand them and collapse them.
- The status bar displays the status of your project and the IDE itself, as well as any warnings or messages.
Tool windows
Android Studio follows your context and automatically brings up relevant tool windows as you work.
- To expand or collapse a tool window, click the tool’s name in the tool window bar. You can also drag, pin, unpin, attach, and detach tool windows.
- To return to the current default tool window layout, click Window > Restore Default Layout or customize your default layout by clicking Window > Store Current Layout as Default.
- To show or hide the entire tool window bar, click the window icon in the bottom left-hand corner of the Android Studio window.
- To locate a specific tool window, hover over the window icon and select the tool window from the menu.
| Tool window | Windows and Linux | Mac |
|---|---|---|
| Project | Alt+1 | Command+1 |
| Version Control | Alt+9 | Command+9 |
| Run | Shift+F10 | Control+R |
| Debug | Shift+F9 | Control+D |
| Logcat | Alt+6 | Command+6 |
| Return to Editor | Esc | Esc |
| Hide All Tool Windows | Control+Shift+F12 | Command+Shift+F12 |
Navigation
- Switch between your recently accessed files using the Recent Files action. Press Control+E (Command+E on a Mac) to bring up the Recent Files action.
- View the structure of the current file using the File Structure action. Bring up the File Structure action by pressing Control+F12 (Command+F12 on a Mac).
- Search for and navigate to a specific class in your project using the Navigate to Class action. Bring up the action by pressing Control+N (Command+O on a Mac).
- Navigate to a file or folder using the Navigate to File action. Bring up the Navigate to File action by pressing Control+Shift+N (Command+Shift+O on a Mac).
- Navigate to a method or field by name using the Navigate to Symbol action. Bring up the Navigate to Symbol action by pressing Control+Shift+Alt+N (Command+Option+O on a Mac).
- Find all the pieces of code referencing the class, method, field, parameter, or statement at the current cursor position by pressing Alt+F7 (Option+F7 on a Mac).
Style and formatting
As you edit, Android Studio automatically applies formatting and styles as specified in your code style settings. You can customize the code style settings by programming language, including specifying conventions for tabs and indents, spaces, wrapping and braces, and blank lines. To customize your code style settings, click File > Settings > Editor > Code Style (Android Studio > Preferences > Editor > Code Style on a Mac.)
Although the IDE automatically applies formatting as you work, you can also explicitly call the Reformat Code action by pressing Control+Alt+L (Opt+Command+L on a Mac), or auto-indent all lines by pressing Control+Alt+I (Control+Option+I on a Mac).
Version control basics
Android Studio supports a variety of version control systems (VCS’s), including Git, GitHub, CVS, Mercurial, Subversion, and Google Cloud Source Repositories.
From the Android Studio VCS menu, click Enable Version Control Integration.
From the drop-down menu, select a version control system to associate with the project root, and then click OK.
Gradle build system
- Customize, configure, and extend the build process.
- Create multiple APKs for your app, with different features using the same project and modules.
- Reuse code and resources across sourcesets.
Multiple APK support
Multiple APK support allows you to efficiently create multiple APKs based on screen density or ABI. For example, you can create separate APKs of an app for the hdpi and mdpi screen densities, while still considering them a single variant and allowing them to share test APK, javac, dx, and ProGuard settings.
Resource shrinking
Resource shrinking in Android Studio automatically removes unused resources from your packaged app and library dependencies
Managing dependencies
Dependencies for your project are specified by name in the build.gradle file. Gradle takes care of finding your dependencies and making them available in your build. You can declare module dependencies, remote binary dependencies, and local binary dependencies in your build.gradle file.
Debug and profile tools
Inline debugging
- Inline variable values
- Referring objects that reference a selected object
- Method return values
- Lambda and operator expressions
- Tooltip values
Performance profilers
Android Studio provides performance profilers so you can more easily track your app’s memory and CPU usage, find deallocated objects, locate memory leaks, optimize graphics performance, and analyze network requests. With your app running on a device or emulator, open the Android Profiler tab.
Memory Profiler
You can use Memory Profiler to track memory allocation and watch where objects are being allocated when you perform certain actions. Knowing these allocations enables you to optimize your app’s performance and memory use by adjusting the method calls related to those actions.
Code inspections
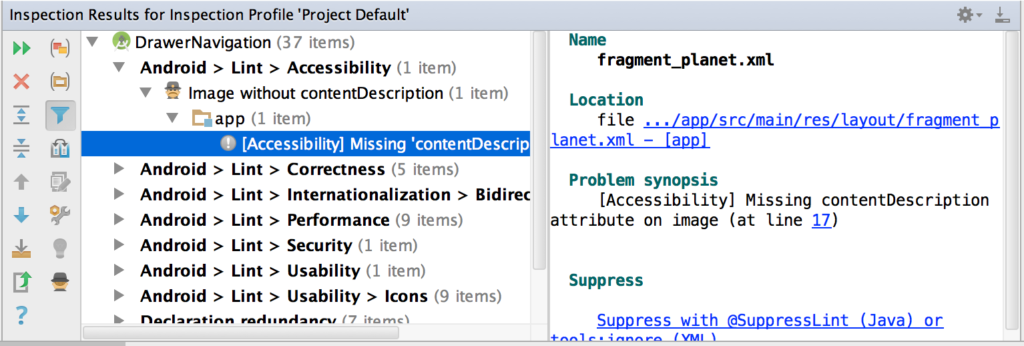
Whenever you compile your program, Android Studio automatically runs configured Lint and other IDE inspections to help you easily identify and correct problems with the structural quality of your code.
The Lint tool checks your Android project source files for potential bugs and optimization improvements for correctness, security, performance, usability, accessibility, and internationalization.
Annotations in Android Studio
Android Studio supports annotations for variables, parameters, and return values to help you catch bugs, such as null pointer exceptions and resource type conflicts.
Log messages
When you build and run your app with Android Studio, you can view adb output and device log messages in the Logcat window.
Performance profiling
If you want to profile your app’s CPU, memory, and network performance, open the Android Profiler, by clicking View > Tool Windows > Android Profiler.
Conclusion: Android Studio is the powerful IDE for developing Android APPS for multiple Android OS-based Devices like Smart Phone, Tab, Smart TV, Wearable Watch, and BT Specific Coding.
Happy Exploring the Android Studio 🙂