It is very important to know about the basics of Android Studio’s file structure.
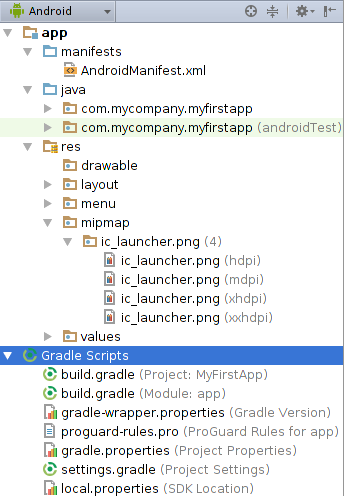
Codable File Structure
- Java: The Java folder contains the Java source code files. These files are used as a controller for controlled UI (Layout file). It gets the data from the Layout file and after processing that data output will be shown in the UI layout. It works on the backend of an Android application.
- drawable: A Drawable folder contains resource type file (something that can be drawn). Drawables may take a variety of file like Bitmap (PNG, JPEG), Nine Patch, Vector (XML), Shape, Layers, States, Levels, and Scale.
Layout File Structure
- layout: A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an Android application. This folder stores Layout files that are written in XML language. You can add additional layout objects or widgets as child elements to gradually build a View hierarchy that defines your layout file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello, I am a TextView" />
<Button android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello, I am a Button" />
</LinearLayout>- colors.xml: colors.xml file contains color resources of the Android application. Different color values are identified by a unique name that can be used in the Android application program.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<color name="colorPrimary">#3F51B5</color>
<color name="colorPrimaryDark">#303F9F</color>
<color name="colorAccent">#FF4081</color>
</resources>- strings.xml: The strings.xml file contains string resources of the Android application. The different string value is identified by a unique name that can be used in the Android application program. This file also stores string array by using XML language.
<resources>
<string name="app_name">GeeksforGeeks</string>
</resources>- styles.xml: The styles.xml file contains resources of the theme style in the Android application. This file is written in XML language.
<resources>
<!-- Base application theme. -->
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar">
<!-- Customize your theme here. -->
<item name="colorPrimary">@color/colorPrimary</item>
<item name="colorPrimaryDark">@color/colorPrimaryDark</item>
<item name="colorAccent">@color/colorAccent</item>
</style>
</resources>Configuration or APP Settings FIle Structure
- AndroidManifest.xml: Every project in Android includes a manifest file, which is AndroidManifest.xml, stored in the root directory of its project hierarchy. The manifest file is an important part of our app because it defines the structure and metadata of our application, its components, and its requirements.
- This file includes nodes for each of the Activities, Services, Content Providers and Broadcast Receiver that make the application and using Intent Filters and Permissions, determines how they co-ordinate with each other and other applications.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.geeksforgeeks.geeksforgeeks">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>build.gradle(Module: app): This defines the module-specific build configurations. Here you can add dependencies that you need in your Android application.
Gradle Structure
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
android {
compileSdkVersion 26
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.example.geeksforgeeks.geeksforgeeks"
minSdkVersion 16
targetSdkVersion 26
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:26.1.0'
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.0.2'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test:runner:0.5'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.2'
}Besides the existing File Structure, Users can add Custom files or folder structures as per the project complexity.
Happy APP Coding 🙂