What is AI ?
Artificial Intelligence = Artificial + Intelligence

Lets elaborate
1-Artificial – made or produced by human beings rather than occurring naturally, especially as a copy of something natural.
2-Intelligence – Intelligence is the ability to learn from experience, adapt to new situations, understand abstract concepts, and use knowledge to manipulate one’s environment. It involves complex cognitive processes like problem-solving, critical thinking, planning, and creativity. While often measured by IQ tests, it is generally considered a multifaceted trait encompassing varied mental capabilities.
Key aspects of intelligence include:
Cognitive Abilities: Reasoning, logic, and processing speed.
Adaptability: The capacity to change behaviors based on new information or environmental demands.
Learning Capacity: The ability to acquire new knowledge and skills.
Types of Intelligence: Beyond general intelligence, this includes emotional intelligence (EQ) and Gardner’s multiple intelligences (e.g., spatial, musical, interpersonal).
Theoretical Models: Includes Spearman’s General Intelligence, Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences, and Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory (analytical, creative, and practical).
Intelligence is both influenced by genetic and environmental factors. It is not a single, universally defined ability, but rather a combination of various cognitive, emotional, and practical skills.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is technology that enables computers and machines to simulate human-like intelligence, allowing them to learn, reason, perceive, solve problems, and make decisions, often by processing vast amounts of data to recognize patterns and perform tasks, from understanding language (like Siri/Alexa) to powering self-driving cars and medical diagnostics.
It utilizes technologies like machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing (NLP) to analyze massive datasets, identify patterns, and perform complex tasks autonomously, such as in self-driving cars, ChatGPT, or virtual assistants.
Core Concepts of AI
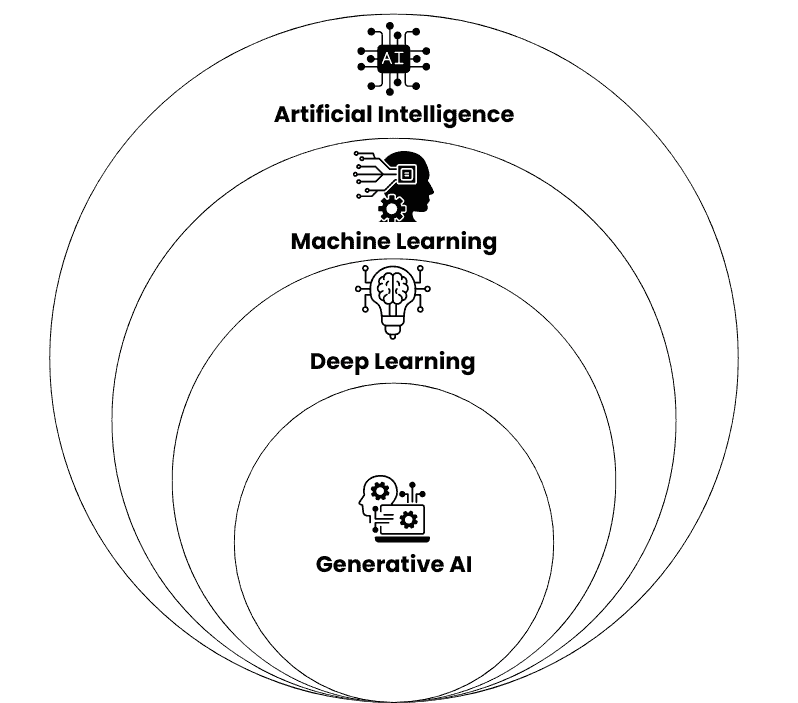
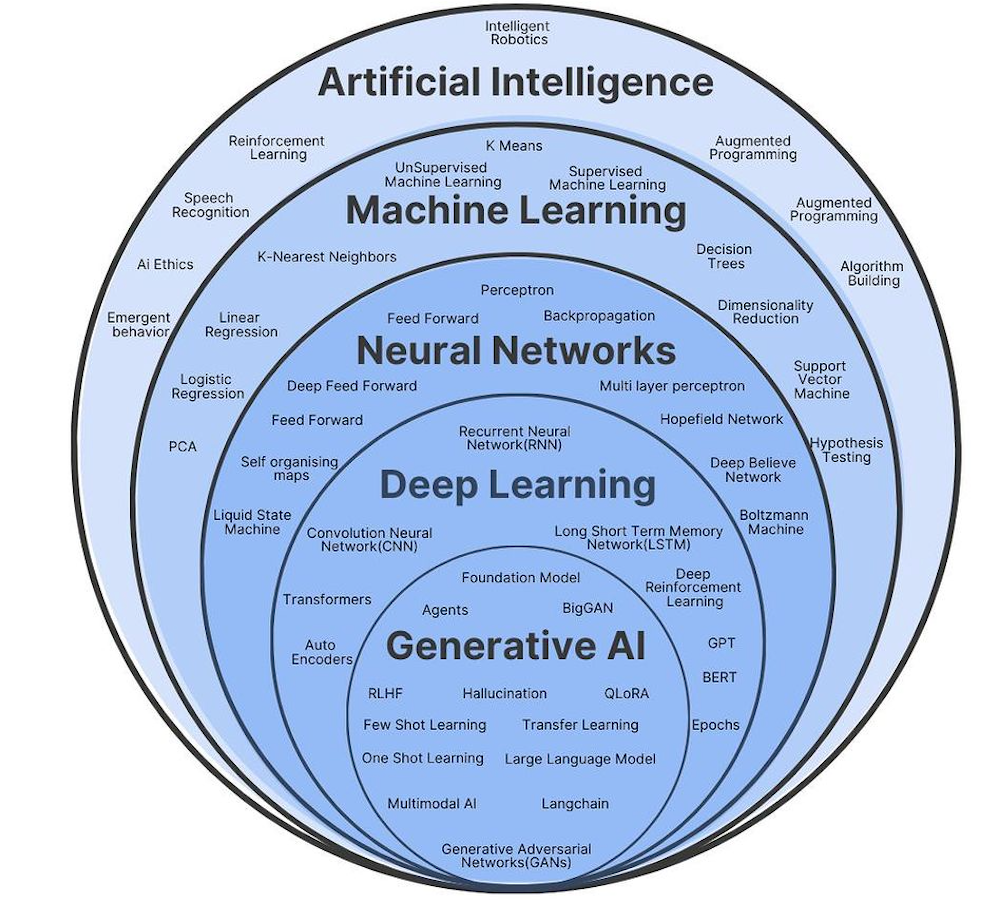
Machine Learning (ML): Systems that learn from data to improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
Deep Learning: A specialized subset of ML using multi-layered artificial neural networks to solve complex problems.
Neural Networks: Algorithms inspired by the human brain, designed to recognize patterns and interpret data.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Technology that allows machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
Computer Vision: Enables machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world, such as image and video recognition.
Common Applications and Uses
Generative AI: Tools like ChatGPT that generate text, images, and code.
Recommendation Systems: Used by Netflix, YouTube, and Amazon to suggest content based on behavior.
Virtual Assistants: Such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, which use voice recognition.
Healthcare: AI aids in analyzing medical images, diagnosing diseases, and drug discovery.
Finance: Used for detecting fraudulent transactions and algorithmic trading.
Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars that interpret surroundings to navigate
Types of Artificial Intelligence
Narrow AI (Weak AI): Designed to perform specific tasks (e.g., facial recognition, internet searches).
General AI (Strong AI): A theoretical form of AI that possesses human-like intelligence across all domains.
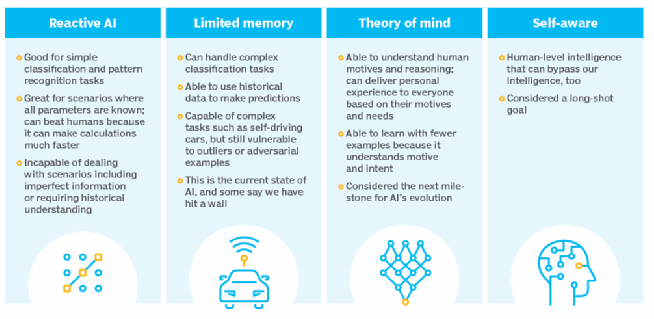
The four types of Artificial Intelligence, categorized by functionality and capability, are Reactive Machines, Limited Memory, Theory of Mind, and Self-Aware AI. These range from basic, non-learning systems to future, self-conscious AI, with current technology mostly limited to the first two types.
Reactive Machines (Type 1): These AI systems are the most basic, performing specific tasks based on immediate inputs without storing past data for future decisions. Examples include IBM’s Deep Blue, which beat Garry Kasparov at chess.
Limited Memory (Type 2): These systems use historical data to make better predictions and decisions,, such as autonomous vehicles that track speed and distance over time. Most modern AI (e.g., chatbots, virtual assistants) falls into this category.
Theory of Mind (Type 3): This is a, still under development, concept where AI can understand human emotions, beliefs, and intentions to interact socially, acting more like a human.
Self-Aware AI (Type 4): This is the final, theoretical stage of AI development, where machines possess their own consciousness, self-awareness, and emotions.
Key Technologies and Tools
AI development often relies on programming languages such as Python, R, Java, C++, and Julia, along with specialized hardware for training models. It is important to distinguish that while all machine learning is AI, not all AI is machine learning
Thank you 🙂


